What Is AI (Artificial Intelligence) ?Definition, Example,How It Works, Real-World Applications & Future.
Introduction
Imagine this: A few months ago, a 28-year-old doctor saved a patient’s life during an emergency, aided by artificial intelligence (AI).
The patient was experiencing a severe heart attack, and there was no time for traditional diagnostic tests.
Yet, the doctor utilized an AI system to quickly analyze the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and blood test results, accurately diagnosing a rare condition.
The AI’s recommended treatment plan led to a successful surgery, and the patient survived, making headlines around the world.

This is just one example of how AI is revolutionizing healthcare.
It not only enhances decision-making beyond the scope of human experience but also enables optimal choices in critical moments.
And this isn’t science fiction.it’s happening today.
Consider another AI revolution: autonomous driving.
In the United States, a completely driverless car is navigating highways.
Using deep learning, the AI system detects a sudden stop ahead, instinctively braking and steering to avoid a collision—faster and more precisely than any human driver, even surpassing professional experts.
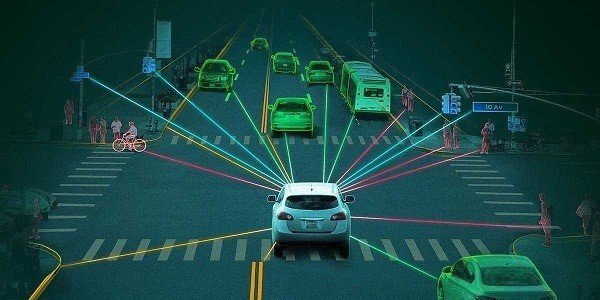
AI is transforming our world at an unprecedented pace, breaking barriers across various industries.
This article will explore the potential of AI, how it works, and how it will shape our future.
Part 1: Defining Artificial Intelligence (AI)
1.What is Artificial Intelligence?
In simple terms, AI refers to the ability of machines to simulate human intelligence, including learning, reasoning, decision-making, and understanding language.
Think of AI as a technology that equips machines with the “ability to think” by processing data and mimicking human cognitive functions.
Example:
Voice assistants like Siri or Google Assistant rely on AI to understand and process voice commands.
When you ask, “What’s the weather tomorrow?”, the assistant uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) to analyze your question and provide the forecast.
AI’s development has evolved from basic rule-based systems to complex deep learning algorithms.
In its early stages, AI could only perform simple, fixed tasks.
Today, with advanced technology, AI can analyze vast datasets and make nuanced, dynamic decisions.
2.Core Goals of Artificial Intelligence
AI aims to make machines more efficient and accurate in specific tasks. Through AI, we can:
- Increase Automation: AI can perform repetitive tasks, reducing human effort and minimizing errors.
- Optimize Decision-Making: AI analyzes large amounts of data to provide better, faster decisions, especially in complex or uncertain environments.
Example: In finance, AI predicts market trends and makes investment decisions based on historical data, news events, and market fluctuations.
Unlike human investors, AI operates around the clock, responding quickly to changes.

Part 2: How Does Artificial Intelligence Work?
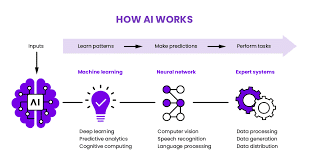
1.Core AI Technologies
AI’s foundation rests on several key technologies:
- Machine Learning (ML): Enables machines to learn from data and recognize patterns to predict future outcomes. For example, Netflix’s recommendation system uses ML to suggest movies based on your viewing history.
- Deep Learning: A subset of ML that simulates the human brain’s neural networks. Google’s AlphaGo, which used deep learning to defeat the world’s best Go player, is a prime example of AI’s decision-making abilities.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Allows machines to understand and generate human language. Siri, for instance, uses NLP to comprehend your voice and respond accordingly.
- Computer Vision: Helps machines process visual information, such as identifying objects in images. Self-driving cars use computer vision to detect traffic signs, pedestrians, and other vehicles.
These technologies bring us closer to achieving AI that emulates human cognition, thanks to machine learning, deep learning, and computer vision.
2.The Relationship Between Data and AI
AI thrives on data. It learns by analyzing massive datasets, adjusting algorithms as it encounters new information.
Example:
In healthcare, AI can analyze thousands of medical images (X-rays, CT scans) to help doctors detect diseases, such as identifying cancer or pneumonia within seconds.
Training and Inference in AI
AI’s learning process consists of two main phases:
- Training: AI systems learn from large labeled datasets. For example, in image recognition, the AI is shown many images of cats and dogs, learning to distinguish them.
- Inference: After training, AI applies its learning to make decisions. For instance, an autonomous car uses its training to navigate roads, detect obstacles, and make driving decisions in real-time.
Part 3: Real-World Applications of AI
AI is making a profound impact across various sectors, enabling capabilities that go beyond traditional computer systems.
Industry Applications
- Healthcare: AI helps doctors diagnose diseases more quickly and accurately.
For example, IBM’s Watson AI analyzes cancer patients’ medical records and genomic data, offering personalized treatment recommendations.
- Finance: AI enhances investment strategies by analyzing big data to predict stock trends and optimize decision-making.
Financial institutions use AI for risk management and real-time trading.
- Transportation & Autonomous Driving: AI powers autonomous vehicles, which collect data via sensors and cameras to make real-time decisions like braking or steering.
Tesla’s autonomous driving system, for example, processes data from its environment to navigate safely.

1.AI in Daily Life
AI is also changing the way we live. Smart home devices like Amazon Echo and Google Home use AI-powered voice assistants to manage household tasks—adjusting temperatures, controlling lights, or playing music based on your preferences.
Example: Online retailers use AI to recommend products by analyzing your browsing and purchasing history. Similarly, news platforms tailor content to your interests based on your reading habits.
2.AI in Creative Fields
AI’s potential extends to the arts. For instance, Google’s Magenta project creates new music compositions based on input melodies.
AI can also generate art, like the app DeepArt, which turns photographs into paintings in the style of famous artists.

Part 4: AI Safety and Risks
While AI offers numerous benefits, it also introduces significant challenges and risks.
Data Privacy and Security
AI systems often require vast amounts of personal data, which can raise concerns about privacy and security.
The Cambridge Analytica scandal, which involved the misuse of Facebook data, highlights the importance of protecting personal information in AI systems.
Technological Transparency
AI’s decision-making processes are sometimes opaque, making it hard to understand how conclusions are reached.
This “black box” issue is particularly relevant in areas like autonomous driving, where it’s challenging to explain AI’s decision to brake or swerve.

Misinformation and Errors
AI models, particularly large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4, can generate persuasive but false information.
This could lead to the spread of misinformation, affecting societal values or influencing public opinion.
Additionally, some AI systems might amplify errors, providing inaccurate advice to non-expert users.
Part 5: The Future of AI
From the Industrial Revolution, which liberated physical labor, to the AI revolution, which will release intellectual capacity, humanity is gradually breaking through its limitations.
The future of AI is beyond measure!
Intelligent Manufacturing: Fully Automated Factories, Workers Transitioning to “Technical Supervisors”
In the future, factories will no longer be places where humans operate machines. Instead, they will be highly intelligent production lines where AI and robots collaborate.
- AI Applications: AI will independently perform a full range of tasks, from precision operations to quality monitoring.
- Career Transformation: Workers will transition from laborers on the production line to technical supervisors and robot managers.
- Impact: This transformation will radically change the labor market. The “labor-intensive” characteristics of traditional manufacturing industries will disappear, and production efficiency and quality will greatly improve.

Autonomous Driving + Unmanned Delivery: A “Humanless” Revolution in the Transportation Industry
The combination of autonomous driving technology and unmanned delivery will completely disrupt the traditional transportation and logistics industries.
- Technological Applications: Freight trucks and unmanned delivery vehicles will replace human drivers, reducing traffic accidents and lowering operating costs.
- Impact on Careers: The profession of driver will almost disappear, and the traditional logistics industry will enter the “humanless” era.
- New Opportunities: New jobs in system maintenance, AI navigation optimization, etc., will emerge.

AI Legal Assistants: From “Paralegal” to “Intelligent Judge”
In the legal industry, AI will not just be a tool for document retrieval, but an intelligent assistant capable of providing legal advice, generating litigation plans, and even making judgments.
- Functions: AI will process complex legal information and provide more accurate solutions than traditional lawyers.
- Impact: AI may act as an “intelligent judge” in some cases, improving judicial efficiency and reducing resource waste.
- Career Transformation: Paralegals will transition into AI system maintenance and legal data analysis experts.
AI-Assisted Creativity: Human-Machine Collaboration Leading the Wave of Artistic Innovation
AI will no longer just be a simple creative tool but will become a “creative partner” for artists.
- Creative Process: AI can generate music, texts, or visual artworks, and even mimic the style of artists.
- Collaboration Mode: Human creators will focus more on emotional expression and creative design, while AI will help bring these ideas to life.
- Industry Impact: Future artistic creations will be a collaborative fusion of human and machine, where innovation and emotional expression will remain the irreplaceable advantages of humanity.
Cross-Disciplinary AI Experts: Knowledge Without Boundaries, Breaking Career Barriers
As AI continues to develop, the boundaries between traditional professions will become increasingly blurred.
- Cross-Disciplinary Collaboration: AI will integrate knowledge from multiple fields to help professionals from different domains make decisions.
- New Career Trends: Future workers will not just be experts in a single field but “AI collaboration experts” with cross-disciplinary and cross-field abilities.
- Industry Innovation: For example, cross-disciplinary cooperation between doctors and data scientists, or lawyers and AI experts, will become common, driving innovation and breakthroughs across various industries.
If you have any insights on AI, feel free to leave your thoughts in the comments section, and let’s discuss together!


